Deep Learning 모델의 작동 과정에서는 보통, 갖가지 방법으로 Human Readable 데이터로부터 특징을 추출하여 Vector 형태로 표현한다. 이미지와 같은 정적 데이터에서는 Feature Extracting라고 하고, 텍스트나 오디오 같은 Sequential 데이터에서는 Embedding이라고 한다. 이렇게 변환된 Vector는 입력 데이터의 중요 특징을 숫자로 표현한다.

Deep Learning 모델에 기반한 검색 시스템을 만들 때에는 새로운 Query를 Pre-trained 모델으로 Vectorize한 후, DB내에 미리 Vectorize한 결과들과 Vector Similarity를 비교하여 가장 가까운 결과들을 리턴한다. Similarity는 가장 간단하게, Cosine Similarity나 Euclidean Distance를 이용한다. 비교 대상이 얼마 없을 때에는 N번 Cosine Similarity를 계산해도 별 문제 없을 수 있지만, 비교 대상이 점점 많아진다면 자연스레 검색에 요구되는 Cost가 높아지고, 검색 소요 시간이 길어진다.
검색 대상을 Vectorize하면서 미리 검색 Index를 만들어서 검색 Cost의 선형적 증가를 최대한 억제할 수는 없을까? Vector Search Engine이 그 일을 대신 해준다. Stand Alone 앱으로는 Qdrant, milvus등의 프로젝트가 있고, Library도 Fiass등 여러가지가 있다. awesome-vector-search에 여러 프로젝트를 정리해놓았으니 참조하면 좋다.
🚀 Qdrant
본 포스트에서 다룰 Qdrant에서는 Qdrant Documentation의 내용을 간략하게 정리한다. 이번 포스트에서는 Qdrant의 핵심 내용인 Collections, Points, Payload, Search에 대해 다룬다.
Qdrant는 Semantic Search, Similar Image / Audio / Video Search, Recommendation Systems에 적합하게 사용할 수 있다.
📥 Install
Docker를 이용하면 아주 쉽게 Stand Alone Qdrant를 설치하고 실행할 수 있다.
1
docker pull qdrant/qdrant
1
docker run -p 6333:6333 -v $(pwd)/path/to/data:/qdrant/storage qdrant/qdrant
위의 명령어로 /path/to/data에 모든 데이터를 저장하며, 6333 포트를 이용하는 Qdrant Instance를 실행할 수 있다.
이후에는 ☸️Kubernetes를 이용해서 Orchestration을 할 수 있다.
📄 Collections
Qdrant에는 크게 두 개의 개념이 있다. 첫번째가 Collection, 두번째가 Point다. Point는 각 Vector 데이터를 의미하며, Collection은 이러한 Point들의 Set이다. 같은 Collection에 속한 Point들은 같은 Dimentionality를 가지며, 같은 metric으로 비교된다. Qdrant는 Vector의 비교에서 가장 흔히 사용되는 아래의 세가지 metric을 제공한다.
- Dot product: Dot - https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dot_product
- Cosine similarity: Cosine - https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cosine_similarity
- Euclidean distance: Euclid - https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Euclidean_distance
Search Engine도 Indexing을 지원하는 일종의 DB로 볼 수 있다. CRUD를 지원한다. Qdrant는 REST API를 통해 거의 대부분의 조작이 가능하다. 자세한 REST API 옵션은 https://qdrant.github.io/qdrant/redoc/index.html#section에 Redoc 포멧으로 잘 설명되어 있으니, 확인하면 좋습니다.
Create Collection
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
PUT /collections/example_collection
{
"name": "example_collection",
"distance": "Cosine",
"vector_size": 300
}
이외의 옵션들은 위에서 언급한 대로 schema definitions와 configuration file에서 확인할 수 있다.
Delete Collection
1
DELETE /collections/example_collection
Update Collection Parameters
Create Collection에서 적용한 Collection Parameter의 개별적 수정이 가능하다. 예를들어, plain-indexing을 허용하는 points들의 최대값을 default 값인 20,000에서 10,000으로 수정하고 싶다면 아래와 같은 명령을 보내면 된다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
PATCH /collections/example_collection
{
"optimizers_config": {
"indexing_threshold": 10000
}
}
🔗 Collection Aliases
Production 환경에서는 새로운 ML모델으로 업그레이드 하는 등의 상황에서 다른 Vector 버전으로 끊김 없이 바꾸어야 하는 상황이 있을 수 있다. Alias를 이용하면 새로운 Vector를 위해 Collection을 리빌드할 때까지 기존 서비스를 중단해야할 필요가 없어진다.
Create Alias
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
POST /collections/aliases
{
"actions": [
{
"create_alias": {
"alias_name": "production_collection",
"collection_name": "example_collection"
}
}
]
}
Remove alias
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
POST /collections/aliases
{
"actions": [
{
"delete_alias": {
"alias_name": "production_collection"
}
}
]
}
Switch collection
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
POST /collections/aliases
{
"actions": [
{
"delete_alias": {
"alias_name": "production_collection"
}
},
{
"create_alias": {
"alias_name": "production_collection",
"collection_name": "new_collection"
}
}
]
}
🔮 Points
Point는 Qdrant에 저장된 Vector값을 의미하며, 각 Point는 필요에 따라 추가적인 Payload 데이터를 구성할 수 있다. Point 데이터의 Modification Operation은 2단계로 수행된다. 첫번째 단계에서는 Operation이 Write-ahead-log에 작성된다. API가 &wait=false 파라미터와 함께 호출되거나 &wait 파라미터가 생략된다면, client는 아래와 같이 “데이터를 받았음”을 의미하는 acknowledgment를 받게 된다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
{
"result": {
"operation_id": 123,
"status": "acknowledged"
},
"status": "ok",
"time": 0.000206061
}
이 Response를 받았더라도 아직 해당 Point가 서비스에 적용된 것은 아니다. Write-ahead-log에 작성된 Operation은 백그라운드에서 비동기적으로 실행된다. 만약 Modification Operation의 즉각적인 적용을 원한다면 API 호출에서 &wait=true flag를 이용해야 한다. 이 경우에는 아래와 같은 Response를 받게 된다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
{
"result": {
"operation_id": 0,
"status": "completed"
},
"status": "ok",
"time": 0.000206061
}
Point IDs
Qdrant는 Point의 id로 64-bit unsigned integers와 UUID를 지원한다.
Upload Points
Point를 업로드할 때에도 역시 REST-API를 이용한다. Qdrant에서는 Batch Loading을 지원한다. 업로드 양이 많을 때는 첫번째 방법을 이용하는 것이 좋다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
PUT /collections/{collection_name}/points
{
"batch": {
"ids": [1, 2, 3],
"payloads": [
{"color": "red"},
{"color": "green"},
{"color": "blue"}
],
"vectors": [
[0.9, 0.1, 0.1],
[0.1, 0.9, 0.1],
[0.1, 0.1, 0.9],
]
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
PUT /collections/{collection_name}/points
{
"points": [
{
"id": 1,
"payload": {"color": "red"},
"vector": [0.9, 0.1, 0.1]
},
{
"id": 2,
"payload": {"color": "green"},
"vector": [0.1, 0.9, 0.1]
},
{
"id": 3,
"payload": {"color": "blue"},
"vector": [0.1, 0.1, 0.9]
},
]
}
Qdrant의 모든 API들은 같은 Method를 복수번 실행하더라도 같은 결과를 낸다. 예를들어, 같은 id에 대한 Upload 명령에는 ‘덮어쓰기’가 된다.
Modify Points
Point의 Vector값 또는 Payload를 수정할 수 있다. Vector값 수정의 경우, 현재(2022년 3월) 기준으로는 재업로드가 유일한 방법이다. 따라서 여기서는 Payload의 수정을 중점적으로 다룬다.
Set Payload
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
POST /collections/{collection_name}/points/payload
{
"payload": {
"property1": "string",
"property2": "string"
},
"points": [
0, 3, 100
]
}
Delete Payload Keys
1
2
3
4
5
6
POST /collections/{collection_name}/points/payload/delete
{
"keys": ["color", "price"],
"points": [0, 3, 100]
}
Clear Payload
Clear를 이용하면 해당 Point의 모든 Payload Key를 삭제한다.
1
2
3
4
5
POST /collections/{collection_name}/points/payload/clear
{
"points": [0, 3, 100]
}
Delete Points
1
2
3
4
5
POST /collections/{collection_name}/points/delete
{
"points": [0, 3, 100]
}
filter를 이용해서 Point의 삭제가 가능하다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
POST /collections/{collection_name}/points/delete
{
"filter": {
"must": [
{
"key": "color"
"match": {
"keyword": "red"
}
}
]
}
}
위의 예제는 Collection에서 { "color": "red" } Payload를 가진 모든 Point를 삭제한다.
Retrieve Points
Point의 id를 이용해서 point 데이터를 얻을 수 있다.
1
2
3
4
5
POST /collections/{collection_name}/points
{
"ids": [0, 3, 100]
}
with_vector 또는 with_payload 파라메터를 이용해서 Point의 Vector값이나 Payload도 함께 리턴받을 수 있다.
1
GET /collections/{collection_name}/points/{point_id}
Scroll Points
Scroll method를 이용하면 id를 모르는 상태에서 모든 Point에 접근하거나, filter를 이용해서 일치하는 Point를 iterate할 수 있다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
POST /collections/{collection_name}/points/scroll
{
"filter": {
"must": [
{
"key": "color",
"match": {
"keyword": "red"
}
}
]
},
"limit": 1,
"with_payload": true,
"with_vector": false
}
위의 API Calldms color = red인 모든 Point를 아래와 같이 리턴한다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
{
"result": {
"next_page_offset": 1,
"points": [
{
"id": 0,
"payload": {
"color": { "type": "keyword", "value": [ "red" ] }
}
}
]
},
"status": "ok",
"time": 0.0001
}
Scroll API는 filter에 매치되는 모든 Point를 page-by-page로 리턴한다. 결과는 Point의 ID를 기준으로 정렬된다. 다음 Page를 Query하기 위해, 현재 Page에서 가장 큰 Point의 ID를 API Call에서 Query의 offset 필드로 입력해야한다. 여기에 입력되어야 할 ID는 Response의 next_page_offset 필드를 보고도 알 수 있다. 만약 Response의 next_page_offset이 null이면 마지막 페이지로서, 다음 페이지가 없음을 뜻한다.
🛒 Payload
Qdrant의 대표적 기능이 바로 Vector에 붙어있는 Payload 개념이다. Payload는 key-value로 구성되고, 각 key는 같은 Type의 여러 value를 가질 수 있다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
{
"colors": ["red", "blue"],
"price": 11.99,
"locations": [
{
"lon": 52.5200,
"lat": 13.4050
}
]
}
Qdrant는 value의 Type을 자동으로 인식하지만, 원한다면 아래와 같이 Type을 명시할 수도 있다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
{
"colors": {
"type": "keyword",
"value": ["red", "blue"]
},
"price": {
"type": "float",
"value": 11.99
},
"locations": {
"type": "geo",
"value": [
{
"lon": 52.5200,
"lat": 13.4050
}
]
}
}
Qdrant에서 이용 가능한 Type은 아래와 같다.
- integer - 64-bit integer in the range -9223372036854775808 to 9223372036854775807.
- float - 64-bit floating point number.
- keyword - string value.
- geo - Geographical coordinates. Example: { “lon”: 52.5200, “lat”: 13.4050 }
같은 key에 해당하는 value는 모두 같은 Type으로 구성되어야 한다.
Payload Filtered Search
Qdrant는 Payload의 Value 기반 검색 기능을 제공한다.
Create Point with Payload
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
PUT http://localhost:6333/collections/{collection_name}/points
{
"points": [
{
"id": 1,
"vector": [0.05, 0.61, 0.76, 0.74],
"payload": {"city": "Berlin", price: 1.99}
},
{
"id": 2,
"vector": [0.19, 0.81, 0.75, 0.11],
"payload": {"city": ["Berlin", "London"], price: 1.99}
},
{
"id": 3,
"vector": [0.36, 0.55, 0.47, 0.94],
"payload": {"city": ["Berlin", "Moscow"], price: [1.99, 2.99]}
}
]
}
Update Payload
Set Payload
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
POST /collections/{collection_name}/points/payload
{
"payload": {
"property1": "string",
"property2": "string"
},
"points": [
0, 3, 100
]
}
Delete Payload
특정 Point의 특정 Payload Key를 삭제할 수 있다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
POST /collections/{collection_name}/points/payload/delete
{
"keys": ["color", "price"],
"points": [0, 3, 100]
}
Clear Payload
특정 Point의 모든 Payload를 삭제할 수 있다.
1
2
3
4
5
POST /collections/{collection_name}/points/payload/clear
{
"points": [0, 3, 100]
}
Payload Indexing
Filter를 통한 검색 효율 증진을 위해, Qdrant는 특정 Payload 필드의 인덱싱 기능을 제공한다. Payload Index는 일반적인 Document-oriented 데이터베이스에서의 방식과 비슷하다.
1
2
3
4
5
PUT /collections/{collection_name}/index
{
"field_name": "name_of_the_field_to_index"
}
Index 설정 후에는 다음과 같이 collection info API에서 제공하는 Payload Schema에 indexed flag를 확인할 수 있다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
{
"payload_schema": {
"property1": {
"data_type": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"indexed": true
},
"property2": {
"data_type": {
"type": "integer"
},
"indexed": false
}
}
}
🔍 Search
Point에 Payload까지 업로드되었다면 이제 유사한 벡터를 찾아내는 Search 기능을 알아볼 차례다.
Similarity Search
많은 현대의 ML 모델들은 실제로 가까운 오브젝트들을 벡터 공간 상에서도 가깝도록 벡터 변환하게 설계되고 학습된다. 아래는 이미지는 쉬운 이해를 돕는다.
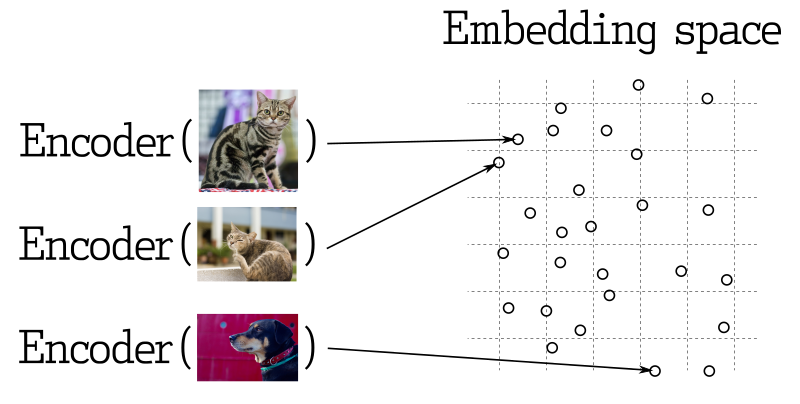
Metrics
‘가깝다’를 정의하는 방법을 Metric이라고 한다. 본 포스트의 최상단에 언급한 대로, 여러가지 Metric이 있다. Qdrant에서는 아래의 가장 자주 사용되는 3가지 Metric을 제공한다.
- Dot product: Dot - https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dot_product
- Cosine similarity: Cosine - https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cosine_similarity
- Euclidean distance: Euclid - https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cosine_similarity
Qdrant는 빠른 연산을 위해 Collection에 입력되는 벡터를 Normalize하고, Dot production으로 변환하는 2단계를 거쳐 진행한다.
Query Planning
Search에서 사용되는 Filter에 따라, Query 실행에 대한 몇가지 가능한 시나리오가 있다. Qdrant는 사용가능한 Index와 Filter 조건의 복잡성, 그리고 Filter 결과의 개수를 고려해서 가장 적합한 Query 실행 방법을 선택한다. 이 과정을 Query Planning이라고 한다.
Query 선택 방법은 상당수 Heuristic에 의존하며 Qdrant 배포 버전에 따라 변할 수 있다.
Search API
Search API는 다음과 같이 실행할 수 있다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
POST /collections/{collection_name}/points/search
{
"filter": {
"must": [
{
"key": "city",
"match": {
"keyword": "London"
}
}
]
},
"params": {
"hnsw_ef": 128
},
"vector": [0.2, 0.1, 0.9, 0.7],
"top": 3
}
위의 예제는 벡터 [0.2, 0.1, 0.9, 0.7]과 가장 유사한 3개의 벡터를 찾아 리턴한다. params는 Search 실행에 사용되는 parameter를 입력한다. hnsw_ef는 HNSW index(Beam Search 알고리즘에서 beam size)를 의미하며, 높을수록 정확하지만 느리다.
filter가 명시되었으므로, filter의 조건을 만족하는 Points들 사이에서만 유사도 계산이 수행된다. filter 작성 방법은 https://qdrant.tech/documentation/filtering를 참조하자.
위 예제의 Response는 아래와 같다. result는 score 순서대로 정렬되어 있다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
{
"result": [
{ "id": 10, "score": 0.81 },
{ "id": 14, "score": 0.75 },
{ "id": 11, "score": 0.73 }
],
"status": "ok",
"time": 0.001
}
Payload in Vector in the Result
Search 실행 시, Default로는 id를 제외한 다른 데이터를 반환하지 않는다. with_vector나 with_payload를 통해 원하는 데이터를 반환받을 수 있다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
POST /collections/{collection_name}/points/search
{
"vector": [0.2, 0.1, 0.9, 0.7],
"with_vector": true,
"with_payload": true
}
with_payload의 경우, 아래와 같이 include 또는 exclude로 반환받을 Field를 제어할 수 있다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
POST /collections/{collection_name}/points/search
{
"vector": [0.2, 0.1, 0.9, 0.7],
"with_payload": {
"exclude": ["city"]
}
}
Recommendtaion API
Negative Vector에 대한 지원은 현재(2022.03) 실험적 기능으로 제공되며, 모든 embedding에 대해 정확한 작동을 보장하지 않는다.
일반적인 검색 뿐만 아니라, Qdrant는 이미 저장되어 있는 데이터들에 대한 검색도 지원한다. 이 API를 이용하면 Neural Network의 Encoder를 이용하지 않고 이미 Encode된 Object를 검색할 수 있다.
이미 저장되어 있는 Vector들을 이용하여 positive_vectors, negative_vectors를 지정하는 방식으로 검색을 할 수 있다. positive_vectors에 가까운 Point는 가중치를 받고, negative_vectors에 가까운 Point는 패널티를 받는다.
positive_vectors, negative_vectors에 사용될 Vector는 ID를 통해 지정하며 아래와 같이 average_vector를 계산해서 그 결과를 기준으로 검색하게 된다.
1
average_vector = avg(positive_vectors) + ( avg(positive_vectors) - avg(negative_vectors) )
아래와 같이 Recommendation API를 호출할 수 있다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
POST /collections/{collection_name}/points/recommend
{
"filter": {
"must": [
{
"key": "city",
"match": {
"keyword": "London"
}
}
]
},
"negative": [718],
"positive": [100, 231],
"top": 10
}
그리고 그 결과는 아래와 같다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
{
"result": [
{ "id": 10, "score": 0.81 },
{ "id": 14, "score": 0.75 },
{ "id": 11, "score": 0.73 }
],
"status": "ok",
"time": 0.001
}